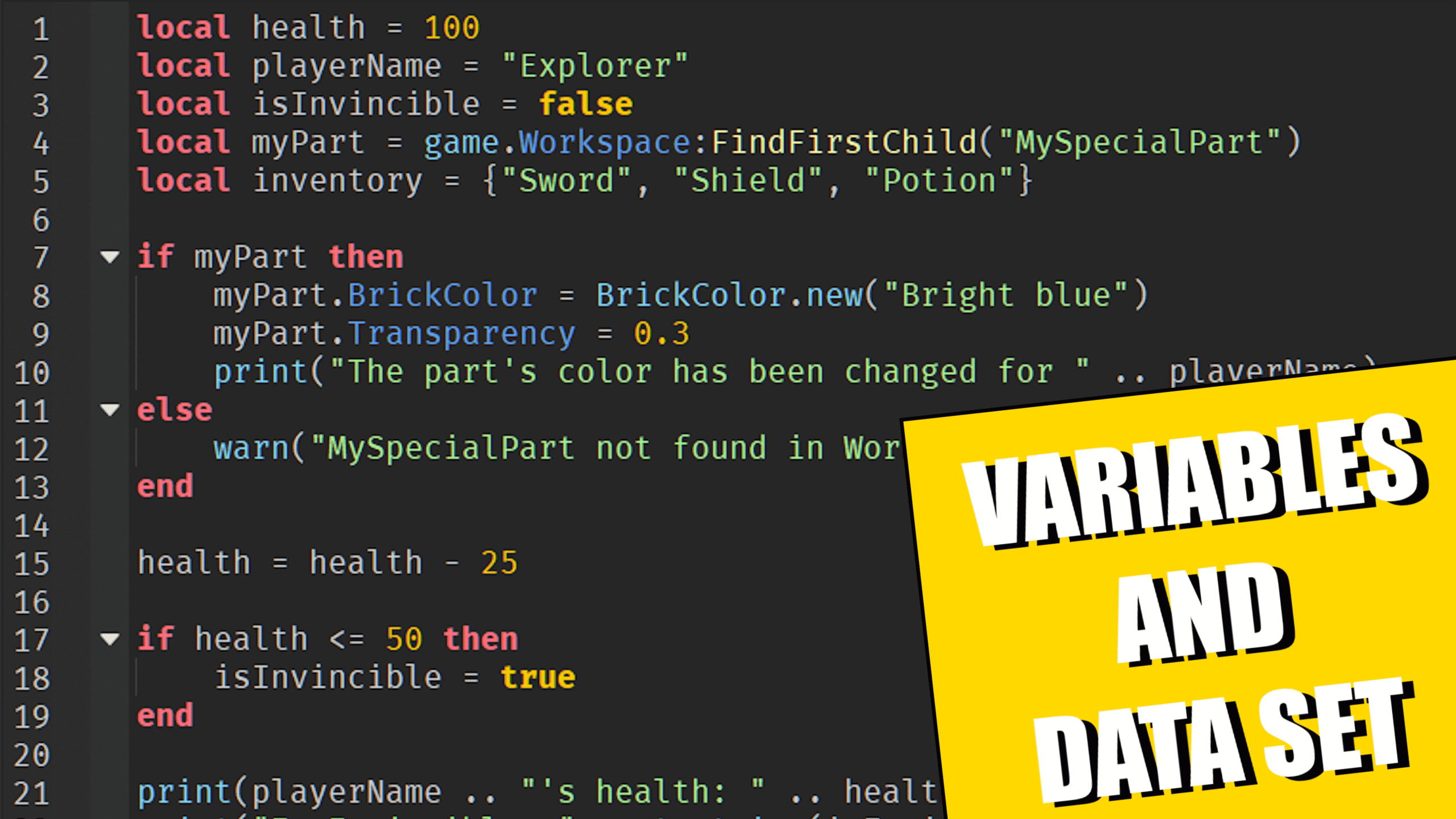
Welcome back to my Roblox beginner scripting tutorial series. We’ll be discussing data types and variables. This is another fundamental concept you need to know to become a better scripter.
Organizing Your Scripts for Better Workflow
For this episode, we’re going to create a new script to keep things organized. As we move forward in this tutorial series, using the same script for everything can get very lengthy and confusing.
Here’s what you should do:
- Go to the Workspace panel in Roblox Studio.
- Find the script you’ve been working on.
- On the right side in the properties panel, find the checkbox labeled Enabled.
- Uncheck it. This disables the script from running when you play the game.
Disabling scripts like this is useful when you don’t want certain scripts to execute during testing or gameplay.
Creating a New Script and Naming It
Next, stop the game if it’s running.
Then, click the + icon next to Workspace and insert a new Script.
Rename the old script to something like printing data types for reference.
Now, rename the new script to variables, matching the topic of this episode.
Understanding What a Variable Is
A variable is basically a reference to another value.
When you create a variable, you’re giving a name to a value, so you can easily refer to that value later using the name instead of typing the value itself multiple times.
Writing Your First Variable in Roblox Lua
Delete any existing code in your new script.
Type the following exactly:
local myVariable = 100
Let me explain what this line means:
localmeans the variable is local to this script.myVariableis the name of the variable — you can name it anything you want.- The
=sign assigns the value on the right (in this case, 100) to the variable on the left.
Printing the Variable’s Value
To see what’s stored in the variable, write:
print(myVariable)
If you run the game and look at the output, you won’t see myVariable, but instead, the number 100.
That’s because the variable myVariable holds the value 100, so printing the variable prints its value.
Why Use Variables?
Imagine if you had to print the number 5 three times like this:
print(5)
print(5)
print(5)
This is repetitive and hard to change later. If you want to change 5 to 10, you’d need to edit every print statement.
Instead, you can store the value in a variable:
local myVariable = 5
print(myVariable)
print(myVariable)
print(myVariable)
Now, changing the variable’s value from 5 to 10 will automatically update every print statement:
local myVariable = 10
This is why variables are powerful — they help you avoid repeating yourself and make your code easier to manage.
Using Variables Efficiently
You can copy and paste the print lines multiple times to see how changing one variable updates all references.
Make sure to delete any extra print statements to keep your script clean.
Naming Conventions: Camel Case
When naming variables, a common convention is camelCase:
- The first word is lowercase.
- Each new word starts with an uppercase letter.
For example:
local myVariableIs50 = 50
print(myVariableIs50)
This makes variable names easier to read and understand.
Fixing Common Errors
If Roblox Studio shows errors like “unknown global variable,” it usually means you mistyped your variable name.
Roblox Studio often suggests corrections, and pressing Tab after typing part of the variable name autocompletes it.
Practice Challenge
For today’s challenge, create several variables and assign them different data types such as:
- Numbers
- Booleans (
trueorfalse) - Strings (text enclosed in quotes)
Write print statements to output each variable’s value.
Conclusion
That’s it for variables and data types. Understanding variables is essential for writing efficient Roblox scripts.
In the next episode, we’ll build on this foundation and explore more scripting concepts.
Thanks for your time, and I’ll see you in the next blog. Take care!